What is a Honey Bee?
Table of Contents
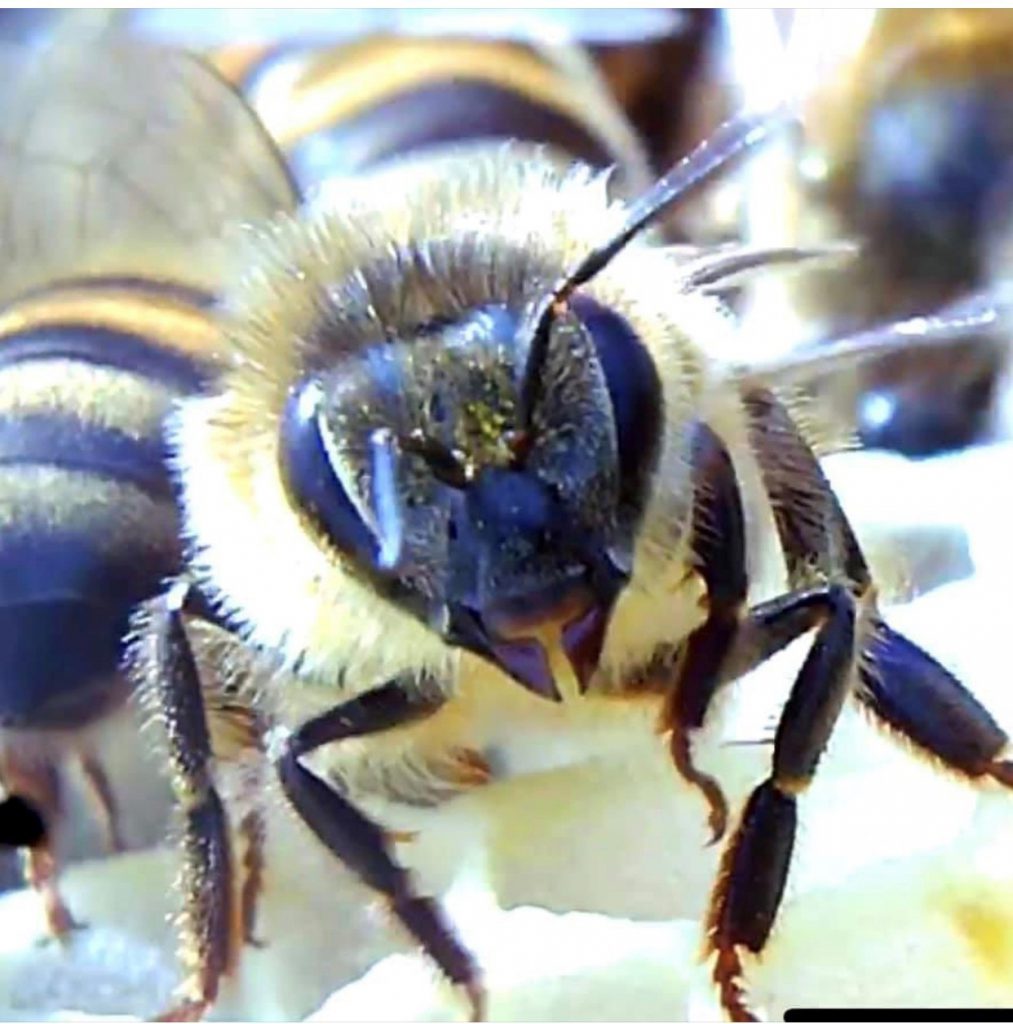

Photo by: KT Brewster

Click Here: Enlarge
Why are Bees Important?
Without the help of bees, you would not have many of the foods you enjoy eating. Bees are needed for growing many types of plants including blueberries, grapes, peaches, apples, watermelons, honeydews, pumpkins, peanuts, and many more.
See Pollination
Have you ever wondered where plants come from? Tiny plants, called seedlings, grow from seeds that have been produced by large plants.
Bees assist in producing plants, seeds, and fruit.
Seeds are produced when the flower is fertilized, when “pollen” is transferred from the male part of the flower, anther, to the female part of the flower, stigma. The bees help in the process of moving pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma of another plant as the bee gathers a sweet syrup called “nectar.” This process is called pollination.
The bees gather and store nectar and some pollen for food.
(Other animals that pollinate are: Birds, bats, butterflies, moths, flies, beetles, wasps, small mammals, and most importantly, bees. The wind also provides pollination for some plants.)

Click Here: Enlarge Chart
There are many types of Bees
There are around 25,000 types of bees in the world, more than 4,000 types of bees in North America, and 400 types of bees in Maryland. Honey bees were brought to North America by the pilgrims to provide pollination for the plants they wanted to grow. The pilgrims did not know that native bees lived in North America and could provide the necessary pollination (see Native Bees)
Many types of bees are considered “Solitary” and live by themselves in straw-like houses. Others, live in tunnels in the ground. Honey Bees live in large colonies, called hives, that may consist of 40,000 to 80,000 bees. Most of the bees, 90-95 percent, are females and perform all the work necessary for them to survive, (gather food, clean, raise more bees).
Winter Months
When the temperature is too cold for honey bees to gather food, they form clusters in the hive and exercise to generate heat. Solitary bees do not survive when the weather gets cold. However, the eggs they have laid, do survive. When spring is near, the eggs hatch and the native bees emerge.
(Understanding the life cycle of native bees
(How Honey Bees Survive Winter by Regulating Their Temperature in a Cluster)
While native bees live only a few weeks to a couple months, the female worker honey bees live approximately 45 days (6 weeks) in the summer and 3-4 months in the winter. The male bees, drones, are born thru the spring and summer. The drones are kicked out in the late fall. The queen can live for 1 to 2 years. When spring is approaching, the hive needs to increase the number of workers, the queen begins laying eggs. She is the only female that can lay fertilized eggs. With the appropriate number of worker bees to support the growth of the hive, the queen can lay 2,000 eggs a day.
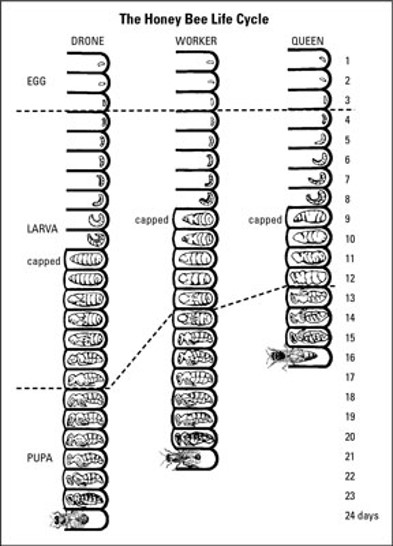
Life Cycle of the Honey Bee:
A honey bee hive consists of approximately 40,000 bees. Approximately, 30,000 are worker (female) bees. 10,000 are drone (male) bees, and one is a queen bee.
Video: Life Cycle of Honey Bees
Once the queen lays an egg in a cell, the egg shell will dissolve in three days. By the fourth day, the egg turns into larvae and grows while the worker bees feed it. In nine days the larvae grows 1,000 times the size it was when the egg was laid. On the tenth day, the worker bees fill the cell with food and cap it. During the next 6-14 days, depending on whether the bee is a queen, worker, or drone, the larvae goes through metamorphosis and becomes a bee. Metamorphosis is the process of great and usually rather sudden change in the form and habits of some animals during transformation from an immature stage (as a caterpillar) to an adult stage (as a butterfly).
Development of the honey bee egg
| Days | Developmental state | Weight | Food source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | egg | 0.132 mg | yolk |
| 2 | egg | not listed | yolk |
| 3 | egg | 0.09 mg | yolk |
| 4 | larva | not listed | royal jelly* |
| 5 | larva | 3.4 mg | royal jelly |
| 6 | larva | 33.3 mg | royal jelly and bee bread** |
| 7 | larva | 100.1 mg | bee bread |
| 8 | larva | 134.5 mg | bee bread |
| 9 | larva | 155.2 mg | bee bread |
Read More: In the Beginning – The Egg
*Royal jelly is a highly nutritious glandular secretion of young bees, used to feed the queen and young brood.
**Bee bread is a fermented mixture of collected pollen and nectar or honey, deposited in the cells of a comb.
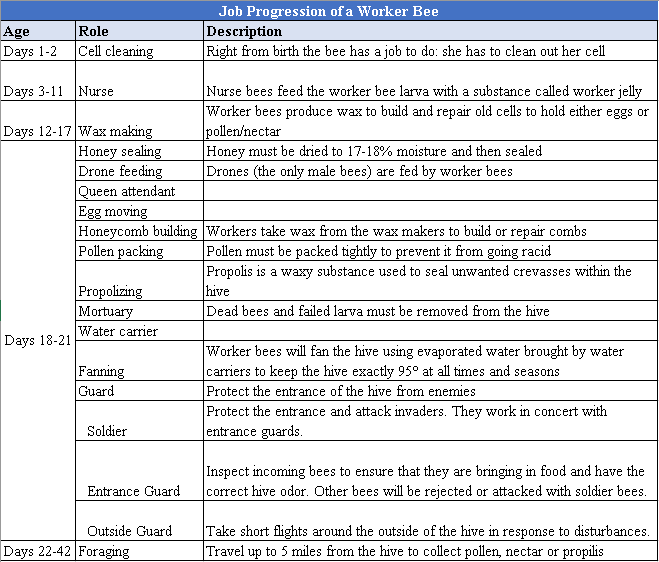
Stages of Life as a Honey Bee
Worker (Female) Bee:
Worker bees are female. They accomplish every chore unrelated to reproduction, which is left up to the queen bee. In their first days, workers tend to the queen. For the remainder of their short lives (just a single month), workers keep busy.
Video: Jobs of the Bee
Newly hatched worker bees are larvae, unable to feed themselves. Worker bees feed their larvae a liquid called "worker jelly," and they eat as many as 800 times a day to build up fat stores. After eight or nine days, larval worker bees spin cocoons and enter the pupal stage. Three weeks later, fully-formed worker bees chew through their cocoons; just a few hours later they’re ready to go to work.
Worker bees also make the decision, when necessary, to relocate the colony in a swarm and then rebuild the new nest.
Maintaining proper temperature for the hive is crucial for the survival of the eggs and larvae. The brood chamber for the bees’ young must remain at a steady temperature to incubate the eggs. If it is too hot, the workers collect water and deposit it around the hive, then fan the air with their wings causing cooling by evaporation. If it is too cold, the worker bees cluster to generate body heat.
Drone (Male) Bee

The drone’s only job is to mate with the queen. Mating occurs in flight, which accounts for the need of the drones for better vision, which is provided by their large eyes. Should a drone succeed in mating, he soon dies because the penis and associated abdominal tissues are ripped from the drone’s body after sexual intercourse.
In the fall in areas with colder winters, worker bees mind the food stores and prevent drones from entering the hive since they are no longer needed, effectively starving them to death.
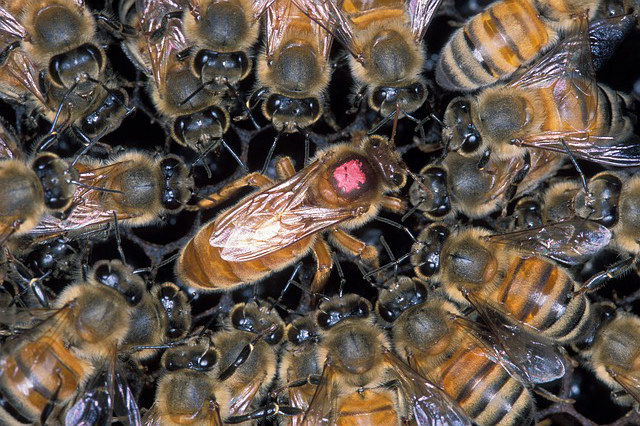

Queen (Mated Female) Bee
There is usually only one queen bee in the hive. She is responsible for laying the eggs and producing all the female and male bees in the hive.
Video: Queen Laying Eggs
Video: Queen and Retinue
A few days after the queen emerges from her cell, she mates with male bees, returns to her hive, and remains there for the rest of her life. A queen can control what eggs are fertilized, to become female bees (workers), and what eggs are not fertilized, to become male bees (drones). The only exception is when the hive becomes overcrowded and produces a swarm. A swarm consists of one-third to one-half of the bees in the hive and the original queen. (See “Swarms” below)
What Does Honey Bees Produce?

Honey:
Earlier, we mentioned, worker bees, called foragers, gather food for the hive.
Video: Harvesting Honey
Video: How Do Bees Make Honey
Video: Honey Tasting
During the gathering of nectar, the worker bees add chemicals to the honey, called “enzymes”, that help transform nectar into honey. The bees carry nectar back to the hive. Nectar consists of three different sugars. Fructose is the main sugar found in honey, followed by glucose and sucrose. The sweet taste of honey is attributed to its higher fructose content, and fructose is known to be sweeter than glucose or sucrose. Nectar, when it arrives at the hive is 60-80 percent water. The bees must evaporate the excess water out of the nectar until it reaches between 17-20 percent water. That is the equivalent of taking a gallon of nectar and evaporating it to one quart. The bees accomplish this task by passing the nectar to other bees and fanning the hive.
Many people have discovered honey has many uses: Sweetener, treat burns, sore throats, as well as others. (see WebMD.com https://www.webmd.com/diet/features/medicinal-uses-of-honey#1 )
(How do Bees Make Honey: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AECtOFpbgVs )
(How to Harvest Honey with Maddie Moate https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnhmxNoo4EY)
(What are the enzymes present in raw honey? Why are they important? https://healthywithhoney.com/what-are-the-enzymes-present-in-raw-honey-why-are-they-important/)
(Enzymes In Honey http://beespoke.info/2013/11/05/enzymes-in-honey/)

Wax:
Honey bees produce a wax that is used to create the six sided cells where the eggs are laid and food is stored.
Video: Honey Bees producing Wax #1
Video: Honey Bees producing Wax
Beeswax consists mainly of esters of fatty acids (fatty acids combined with alcohol), but over 200 other minor components have been identified in beeswax. It requires 6-8 pounds of honey to make one pound of wax. Beeswax is gathered by the beekeeper when he harvests the honey. Once the beeswax is collected, washed, and strained, it can be used to make candles, (Beeswax candles burn brighter, remove toxins from the air and give off a sweet, warming honey scent.) Beauty and Personal Care Products. Beeswax is used in beauty and personal care products such as lip balm, hand cream.
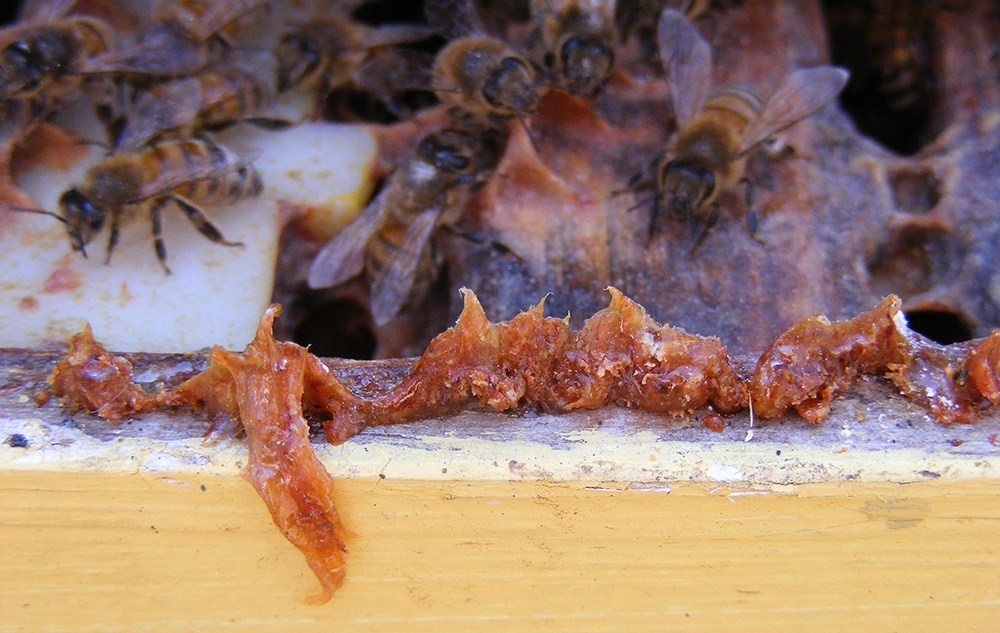

Propolis
According to WebMD.com, Propolis is a glue and filler-like substance, made from tree sap and pollen. The bees use it to seal the hive and protect from diseaseas.
Video: What is Propolis
Propolis is used for diabetes, cold sores, and swelling (inflammation) and sores inside the mouth (oral mucositis). It is also used for burns, canker sores, genital herpes, and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
How does it work?
Propolis seems to have activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It might also have anti-inflammatory effects and help skin heal.
- Diabetes. Research shows that taking propolis may improve blood sugar control by a small amount in people with diabetes. But it doesn’t seem to affect insulin levels or improve insulin resistance.
- Cold sores (herpes labialis). Most research shows that applying an ointment or cream containing 0.5% to 3% propolis five times daily helps cold sores to heal faster and reduces pain.
- Swelling (inflammation) and sores inside the mouth (oral mucositis). Most research shows that rinsing the mouth with a propolis mouth rinse helps heal sores caused by cancer drugs or dentures.

Swarms
When a hive becomes overcrowded, some of the bees must leave or the hive will not be able to survive. The queen will lay eggs that will become a replacement queen. After a few days, half of the bees in the hive and the original queen will leave and search for a new home.
Video: Why do Bees Swarm
Video: Catching a Swarm
The swarm will land on a nearby branch, building, fence, car, or any other surface. A few bees will search for a new home. Once they find a satisfactory home, they will tell the swarm. All the bees will then follow the search bees to the new home.
A swarm is nature’s way in which a colony of bees expands. Because the swarm does not have a hive to protect, the bees are very docile. The bees form a curtain around the queen to protect her while they look for the new home. Before the workers leave their original hive, they gorge with honey so they have the resources to start their new home.
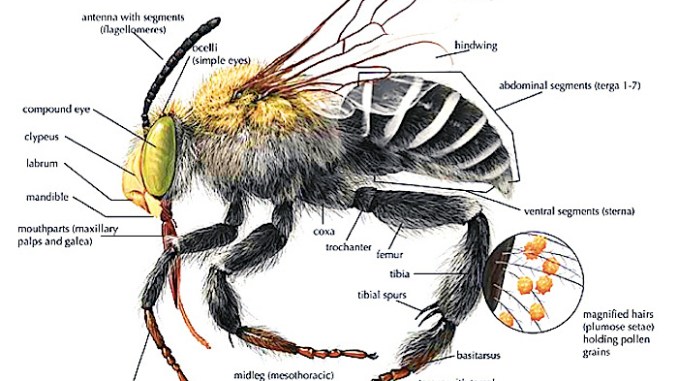
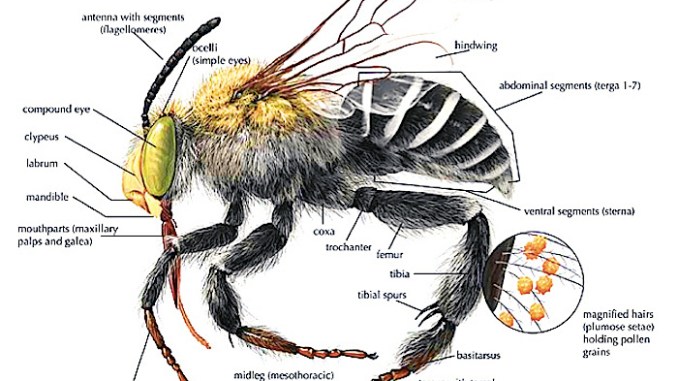
Physiology of a Bee?
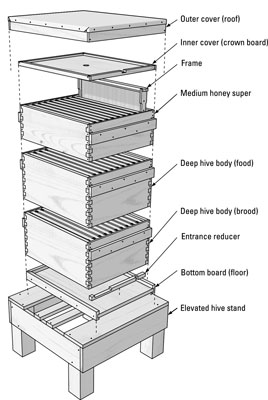
So you are thinking about keeping honey bees.
How to begin.:
- Research any local government and Covenant restrictions associated with honey bees.
- Find a local bee organization that provides a class on "Beginning Beekeeping". Take the class. You will increase your chances of success and satisfaction. And you will spare yourself unnecessary costs, efforts, and losses.
- Research the cost (Note: It is suggested to begin with two hives.)
- Equipment, per hive: ($200-$300 for woodenware).
- Each Package of honeybees $120-$150 per 3 pound package of honeybees.
- Tools and suits: $100-$200
- Find a mentor. Many clubs, such as Howard County Beekeepers Association provide mentors with membership and taking their "Beginning Beekeeping" class.
- Commit to managing the honey bees as required.
- Commit to researching bee diseases, traits, new techniques.
Honey Bees Under a Microscope

Photos of a honey bee using an electron microscope, Smithsonian.